Ready to use legal template
Work on without any hassle
Compliant with Filipino law
Ready to use legal template
Work on without any hassle
Compliant with Filipino law
Home › Accounting › General receipt
Learn more about General Receipt in Philippines
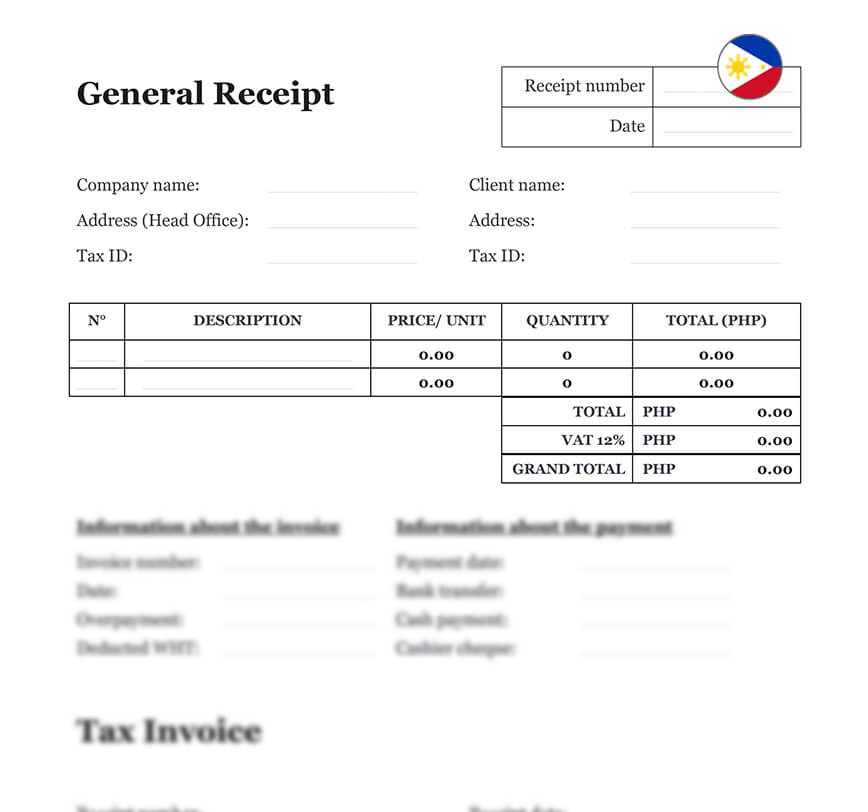
A General Receipt is a written document that acknowledges the receipt of money, goods, or services between two parties. Whether used for one-time payments, sales of goods, refunds, or service fees, a general receipt provides legal proof of the transaction and can support accounting, tax filings, and internal audits. It typically includes the date, amount received, payer and payee details, description of the transaction, and signatures of both parties. In many cases, issuing a receipt is also required under the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) regulations. Download our General Receipt Form, professionally drafted for legal and practical use in the Philippines. It’s easy to edit in Word format and ensures your transactions are properly documented and compliant with local standards.
Table of contents
-
What is a General Receipt?
-
How to issue General Receipts in the Philippines?
-
What is the importance of General Receipts for Businesses?
-
What are the common mistakes to avoid when issuing General Receipts?
-
What are the BIR Regulations for General Receipts in the Philippines?
-
How to keep accurate records of General Receipts?
-
What is the role of General Receipts in the taxation system of the Philippines?
What is a General Receipt?
A General Receipt in the Philippines is a document issued by a seller to a buyer as proof of payment for goods or services. It typically includes the date of the transaction, the name and address of the seller and buyer, a description of the goods or services purchased, the amount paid, and the mode of payment. The issuance of a General Receipt is required by law under the National Internal Revenue Code (NIRC) and the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) regulations. Failure to issue a General Receipt may result in penalties and legal consequences. Overall, a General Receipt serves as a record of transactions and a proof of purchase, promoting transparency and accountability in business transactions in the Philippines.
How to issue General Receipts in the Philippines?
Issuing General Receipts in the Philippines is a simple process that can be done manually or electronically. Here are the basic steps to issue a General Receipt:
1. Start by preparing the necessary details such as the date of the transaction, the name and address of the buyer and seller, and a description of the goods or services purchased.
2. Determine the total amount of the transaction, including any taxes or fees that apply.
3. Write or print the information on a pre-printed General Receipt form or create one using a computer or mobile device. The form should include a sequential receipt number for record-keeping purposes.
4. Provide a copy of the General Receipt to the buyer and keep a copy for your records. If the transaction is made electronically, you can email the receipt to the buyer or provide a printed copy if necessary.
5. Make sure to store the original and duplicate copies of the General Receipt properly, as required by the BIR regulations. Electronic receipts should be saved in a secure location and backed up regularly.
6. Finally, ensure that the General Receipt complies with the BIR requirements, such as the use of a registered receipt format, the inclusion of a tax identification number, and the accurate recording of the transaction details.
By following these steps, businesses and individuals can issue General Receipts in the Philippines and stay compliant with the tax regulations.
What is the importance of General Receipts for Businesses?
1. Legal Compliance
The Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) requires businesses to issue General Receipts for every sale, barter, or exchange of goods or services. Failure to comply with this requirement may result in penalties, fines, and legal consequences.
2. Proof of Sale
General Receipts serve as proof of sale and a record of transactions. They provide evidence that the buyer has paid for the goods or services and that the seller has received the payment.
3. Taxation Purposes
General Receipts help businesses keep accurate records of their sales and revenues, which is crucial for tax compliance. The BIR uses General Receipts to verify the accuracy of tax returns and ensure that businesses pay the correct amount of taxes.
4. Customer Service
General Receipts provide customers with proof of purchase and serve as a guarantee for the goods or services received. They also allow customers to claim refunds or warranties in case of product defects or dissatisfaction
5. Business Analysis
General Receipts can be used to analyze business performance, such as tracking sales trends, identifying popular products or services, and forecasting future revenue.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when issuing General Receipts?
1. Failure to issue a General Receipt: One of the most common mistakes is failing to issue a General Receipt for a sale or transaction. This is a violation of BIR regulations and can result in penalties and legal consequences.
2. Inaccurate or incomplete information: Another common mistake is providing incomplete or inaccurate information on the General Receipt, such as the wrong date, amount, or description of the goods or services purchased. This can lead to confusion and disputes with customers, as well as problems with tax compliance.
3. Use of unregistered receipt format: Businesses should use a registered receipt format approved by the BIR. Using an unregistered format can result in penalties and fines.
4. Missing or incorrect tax identification number (TIN): The TIN of both the seller and the buyer should be included on the General Receipt. Failure to provide the correct TIN can lead to problems with tax compliance and verification.
5. Failure to keep proper records: Businesses should keep a copy of the General Receipt for their records and submit duplicate copies to the BIR as required. Failure to keep proper records can lead to problems with tax compliance and audits.
By avoiding these common mistakes and following the BIR regulations, businesses can ensure that they issue accurate and compliant General Receipts.
What are the BIR Regulations for General Receipts in the Philippines?
The Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) has several regulations regarding the issuance of General Receipts in the Philippines. Here are some of the most important regulations:
| ➤ Mandatory Issuance: Businesses are required to issue General Receipts for every sale, barter, or exchange of goods or services. Failure to comply with this requirement may result in penalties, fines, and legal consequences. |
| ➤ Registered Receipt Format: Businesses must use a registered receipt format approved by the BIR. The format should contain the business name, address, and Tax Identification Number (TIN), as well as a sequential receipt number and the date of the transaction. |
| ➤ Accurate Information: The General Receipt should contain accurate and complete information, including the date of the transaction, the name and address of the buyer and seller, a description of the goods or services purchased, the amount paid, and the mode of payment. |
| ➤ Proper Record-Keeping: Businesses should keep a copy of the General Receipt for their records and submit duplicate copies to the BIR as required. The General Receipts should be kept for at least three years. |
| ➤ Correct TIN: The TIN of both the seller and the buyer should be included on the General Receipt. The TIN should be accurate and should match the records of the BIR. |
| ➤ Use of Cash Register Machines (CRM): Businesses that use CRM must secure a permit from the BIR and comply with the guidelines set by the agency. The CRM should be capable of generating accurate and complete receipts, and should be registered with the BIR. |